Renewable energy: A baggage or boon for Karnataka?
By EPR Magazine Editorial June 12, 2020 10:48 am IST
By EPR Magazine Editorial June 12, 2020 10:48 am IST

As on 30th April 2020, Karnataka became the first state in India with more than 50 percent of renewable energy in its installed capacity. The government of India is aggressively pursuing the addition of renewable electricity generation sources into installed capacity. In accordance with this, state governments are actively adding more renewable energy into the installed capacity. This article discusses the issues with high renewable energy penetration in installed electricity generation capacity and the issues associated with it.
Table 1 presents the installed electricity capacity of Karnataka as on 30th April 2020. The total installed electricity generation capacity of Karnataka is 29,825 MW. In this, 15,232 MW, i.e., 51 percent of installed capacity comprises renewable energy sources like solar, wind, cogen, biomass, and mini hydel. Solar and wind energy are the major contributors to the renewable energy portfolio with 7,274 MW and 4,855 MW respectively. With this, “Karnataka becomes the first state in India to have more than 50 percent renewable electricity generation contribution in its installed capacity.” If large hydro is also considered under renewable energy sources portfolio, then its percentage is as high as 63 percent in the installed capacity.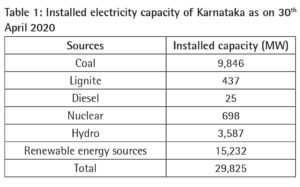
However, the average peak demand of Karnataka during the lockdown was around 10,400 MW, i.e., just 35 percent of the total installed capacity. During the same period last year, the average peak demand was around 12,000 MW and that too accounts for just 40 percent of the total installed capacity. Moreover, this being summer, the electricity demand is expected to be on the higher side. During monsoon and winter months, the peak demand is expected to be reduced and will be around 8,500 MW and the result is even more idle generation capacity.
As things stand, renewable energy alone should be able to meet the electricity demand of the state. However, in reality, that is not possible due to the variability associated with renewable energy technologies. Solar power can generate electricity only during the daytime and wind energy can generate electricity only when there is wind. Nearly 60 percent of Karnataka’s electricity generation capacity is lying idle throughout the year. With more than adequate available electricity generation capacity, many of the conventional power plants are sitting idle incurring heavy losses to the state electricity utilities. The nationwide lockdown has increased these potential losses with more reduction in electricity demand and more increase in idle installed electricity capacity.
During the daytime when solar power is available, the generation from conventional coal power plants is reduced and once solar power goes off, these conventional power plants are ramped up to meet the electricity demand. The same is applicable to wind power, too. Especially during the monsoon season, the generation from wind power will be very high and the rest of the time, the generation is very low. With more renewable energy in installed capacity, there is more loss to conventional power plants due to its non-functioning.
Some of the reasons for increased idle generation capacity are that peak demand has not increased in the expected lines, and renewable energy being flexible, there is essential need for adding stable conventional generation into the electricity system as backup. So, with addition of renewable energy installed capacity, the coal installation has not stopped, and it is also on the increasing side. To conclude, with more renewable energy in installed capacity, Karnataka has more than adequate sources to meet the electricity demand. The more renewable energy sources have resulted in more idle electricity generation capacity to the system. So, during all the days in a year, these are non-performing assets and it incurs huge losses to the utilities both in the short and longer run. Being the first state in India with more than 50 percent of renewable energy in its installed capacity, the Karnataka experience is a loss to the concerned stakeholders as it stands.
Authored by:
Dr. Balasubramanian S., Researcher,
Department of Management Studies, Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.