Evaluating the harmonics study for a solar plant
By EPR Magazine Editorial April 7, 2022 11:49 am IST
By EPR Magazine Editorial April 7, 2022 11:49 am IST
Grid-connected PVs, coupled with nonlinear loads and bi-directional power flows, impact grid voltage levels and total harmonic distortion (THD).
Renewable Energy (RE) sources differ from conventional power generation sources. Therefore, integrating such variable sources into electrical networks requires special consideration.
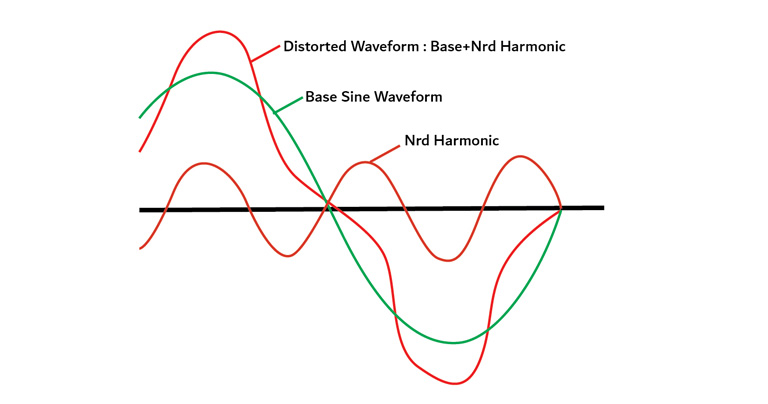
Photovoltaic systems are inverter-based generators that consist of photovoltaic panels that generate direct current (DC) power and an inverter that continuously transforms the DC power into alternating current (AC) power. Just like other electronic equipment, photovoltaic inverters inject harmonics into the connected electrical installation. This leads to overheating and accelerated ageing of the electrical assets. It also results in unplanned outages.
Grid-connected PVs, coupled with nonlinear loads and bi-directional power flows, impact grid voltage levels and total harmonic distortion (THD). A low-voltage (LV) distribution feeder further creates distortion in the power system. Consequently, components of LV distribution systems such as switchgear, cables, and circuit breakers are subjected to distorted load current, resonance, overheating, etc. In addition, high-frequency distortions can interfere with communications and signalling systems, causing inaccurate measurements of sensors. These issues impact equipment reliability, asset life, and operating costs, and thus, the overall operational performance of the PV generating system. As relays generally work in the power frequency range, they cannot efficiently resolve high-frequency problems. Additionally, the photovoltaic system is composed of a DC source, which may increase the challenge of tackling residual DC current and corrosion. So, other comprehensive techniques have to be studied to achieve the safe and reliable operation of power systems.
IEEE Standard 519-1992 [2] specifies the allowable limits of harmonics in the grid, whereas, IEEE Standard 1547-2003 [3], focuses on the interconnection requirements of renewable resources. Designing and modelling electrical systems in conformance with these standards can deliver cost-effective, stable, and reliable grids. The filtering of harmonics needs to be carefully designed to maintain the control bandwidth of the inverter. It is also necessary to provide clean and reliable control signals in analog and digital electronic circuits.It is essential to perform studies such as harmonic studies and power quality studies with modelling and simulation to interpret the implementations as per required standards. Based on the studies mentioned above, designing harmonic filters and repurposing capacitors may be considered to achieve effective PV penetration. Such an approach will provide mitigation solutions that lead to more PV penetration without sacrificing the safety and reliability of the distribution system. We can also adapt the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) technique simulation to eliminate lower order harmonics in the motor current, low-speed torque pulsation, and cogging effects, thus enhancing the power inverter’s performance.
Both nonlinear loads and PV systems significantly impact the distribution systems’ power quality. To ensure high quality power from PV systems, power system security, and grid stability, some new power quality requirements are imposed by different grid codes and standards. Power quality assessments for existing and new PV plants will investigate the gaps present in the power system and provide suitable, implementable solutions to mitigate the issues found during the investigation.
Manav Energy has completed many studies on harmonics, power quality, and power systems in the renewable sector worldwide. Moreover, it has designed various PV systems and integrated them into national grids.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.